American Tulipwood/Yellow poplar



Botanical name: Liriodendron tulipifera
Common/commercial names: Yellow poplar (USA), tulip poplar (USA), canary whitewood
Distribution & Availability
Widespread throughout Eastern USA. Widely available in a full range of standard lumber thicknesses. Excellent availability as lumber and veneer. Tulipwood is one of the largest trees in the U.S. forest and can produce very wide and long specifications, which are relatively knot free. It represents around 9% of the standing hardwood resource, which ensures continuity and volume supply to export markets.
General Description
The sapwood is creamy white and may be streaked, with the heartwood varying from pale yellowish brown to olive green. The green colour in the heartwood will tend to darken on exposure to UV light and turn brown. The wood has a medium to fine texture and is straight grained. The size of the sapwood and some physical characteristics will vary according to growing regions. The wood has many desirable characteristics and is suitable for a wide variety of important uses. Tulipwood is not a poplar (Populus) and has many superior properties. However the tree resembles the shape of the European poplar, hence its name in the USA.
Physical & Mechanical Properties

A medium density wood with low bending, shock resistance, stiffness and compression values, with a medium steam bending classification. Tulipwood is very strong for its weight and is ideal for laminated beams and structures. More detailed strength information is available in the AHEC publication Structural design in American hardwoods.
Working Properties
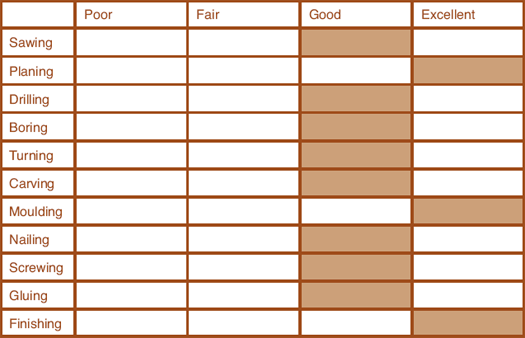
A versatile timber that is easy to machine, plane, turn, glue and bore. It dries easily with minimal degrade. It has very good dimensional stability and has little tendency to split when nailed. It takes and holds paint, enamel and stain exceptionally well.
Durability
Non-resistant to decay. Heartwood is moderately resistant to preservative treatment, sapwood is permeable. The absorptive properties of tulipwood mean that it is potentially ideal for preservative treatment. Recent research in Europe confirms that tulipwood works effectively with traditional and new preservative treatment methods. For more information visit: www.americanhardwood.org.
Main Uses
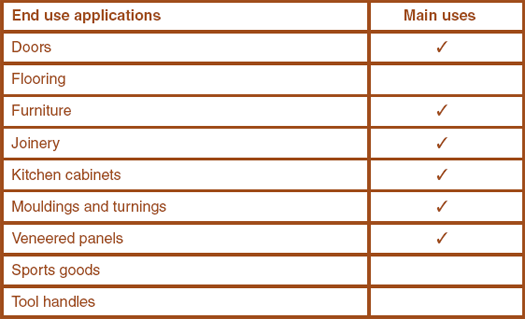
Construction, furniture, interior joinery, kitchen cabinets, doors, panelling, mouldings, edged-glued panels, plywood (USA), turning and carving.
Other Information
This very available, cost effective and versatile American hardwood is exported around the world and many designers and architects are exploring its exciting natural colour variegation. Burls and swirls in the grain are a common occurrence and are not considered defects. A heavy purplish-blue mineral colour is limited in the upper lumber grades and unlimited in the Common lumber grades. Because the Common grades are generally stained or painted in finishing, a grey colour is allowed in the wood after surfacing. Tulipwood is becoming more readily available in fixed widths. Note that tulipwood is widely known as yellow or tulip poplar in the USA.
